The Secret Sauce of Functional Training
What makes functional training functional?
The How and The Why behind our Functional Training Design.
Let's start with our definition of functional training. Functional training is an ongoing exercise program (not just a single workout) with the purpose of improving the way you move everyday and live your life. It's equally useful for someone seeking to improve activities of daily living, as much as for someone trying to get better at their recreational activities, or for someone trying to reach the podium in a sporty competitive activity.
Layers of the onion.
At the most basic level, human movement can be placed in 3 movement categories: locomotion, manipulation, and striking.
- Locomotion is moving yourself from one place to another - walking, running, riding, climbing, etc.
- Manipulation refers to moving objects - pushing, pulling, lifting, and carrying things.
- Striking is applying movement to objects to make things happen. In sporty activities think swinging rackets and clubs or kicking soccer balls. Around the house, think swinging hammers, chopping wood, or shoveling snow. Striking can also refer to punching and kicking in a combative sense.
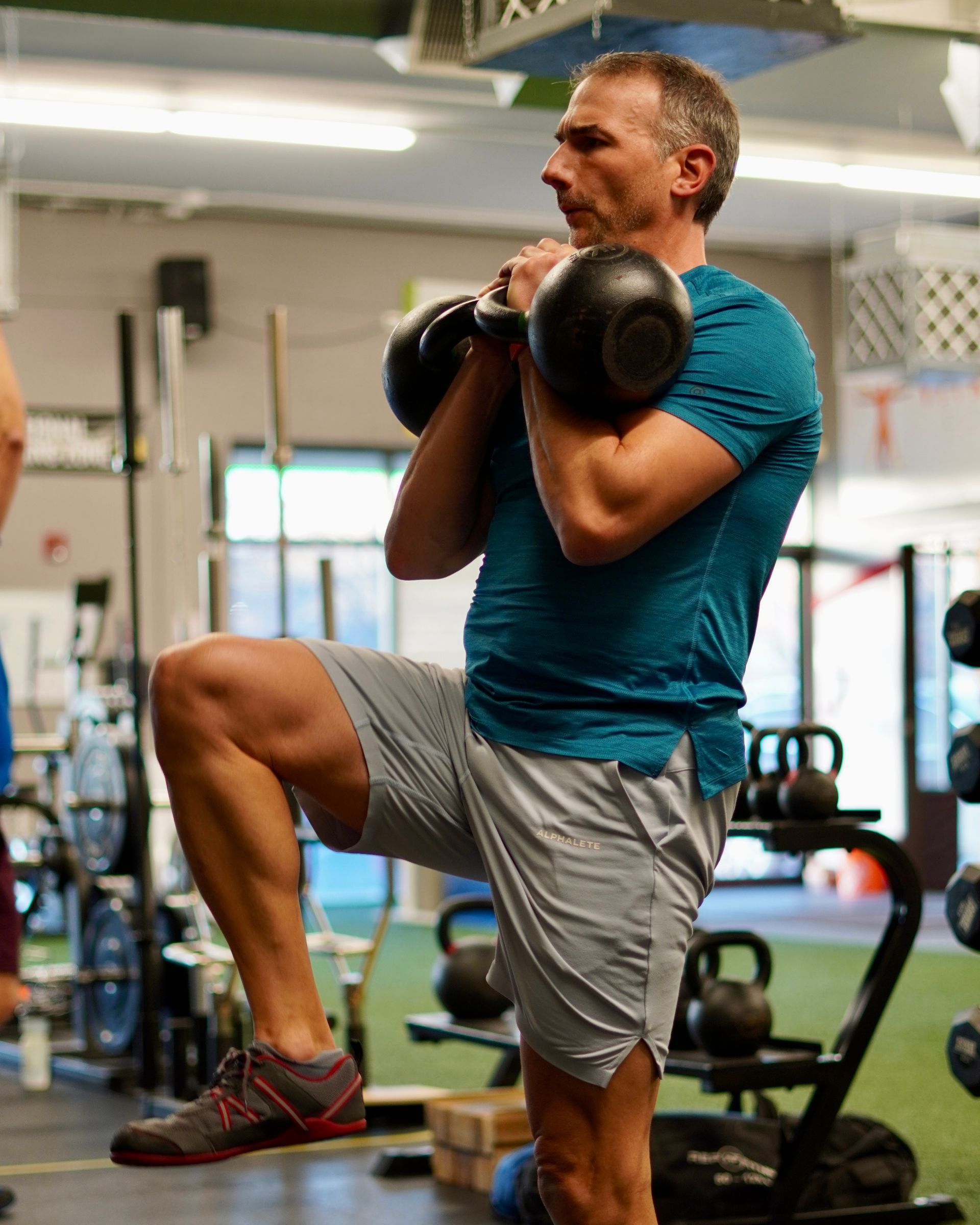

The focus of the training is always on functional movement. So, our exercises are selected with the intent to move in patterns, not parts. Lifting and carrying objects, running across the street, or shoveling for example, all require an organized effort from multiple joints and muscle groups plus several other body systems such as the nervous, skeletal, endocrine, respiratory, and circulatory systems.
Exercise Categories.
The next layer of the onion is how we categorize specific exercises. And while each of these categories often focus on one joint, none of them ever act in isolation in functional training.
Categories:
- Knee Dominant - knee bending is the predominant action
- Hip Dominant - hip hinging is the predominant action
- Pushing - arms pushing objects away from the body
- Pulling - arms pulling things toward the body
- Rotating - this is twisting and twist-resisting
To illustrate the point that nothing exists in isolation, an exercise that is knee dominant (like a goblet squat) always recruits your core, your shoulders, your grip, your breath, your senses, your hormones, your blood, your bones, and all the muscles above and below the knees. But the big knee-bendy thing going on is how we categorize the movement.
Here's the secret combination.
Putting it all together, every workout in every training phase at Vitruvian Fitness will have the following types of exercises:
- 1 Knee Dominant (e.g. squat or lunge)
- 1 Hip Dominant (e.g. glute bridge or deadlift)
- 1 Horizontal or Vertical Push (equal amounts over a period of time) (e.g. push up or overhead press)
- 2 Horizontal or Vertical Pulls (usually one of each) (e.g. row or pull down)
- 1 Rotation or Anti-Rotation (e.g. cable twist or Paloff press)
And because work without rest is a wasted effort, we rest between exercises. But we don't have all day, so we rest actively. That means we do a non-competing exercise while resting the parts that just did their work. For example, after doing a knee dominant exercise, we follow it with a push followed by a pull and so on, which lets the legs rest up for their subsequent efforts. By the time we've done a round of five or six exercises, each of the muscle groups get plenty of rest by the time it's their turn to go again.
Obviously there's a little more to it than that but once you've selected the different exercises, what's left to determine is complexity, volume, load, tempo, intensity, duration, and supplemental movement development. Easy right?
Here's an article about the different types of training phases and what each seeks to accomplish. And here's an article about balancing strength training and cardio throughout a typical week.
Why.
As you start to put all this together, you may begin to realize why life just seems easier and more fun. The hills don't seem so steep and high. The babies we're raising don't seem to be getting heavier even though we see them getting bigger. The fatigue after a weekend of yard work feels like a reward, not a punishment. After a vigorous game of sportsball, you feel like you could go again tomorrow. You look forward to the praise you receive at your annual check-ups. You look forward to new adventures.
Those are the benefits of functional training.
Curious to learn more?
We encourage you to do a 30-Day Trial Membership. In 30 days, you will get a 1-on-1 introductory onboarding session with Functional Movement Screen® plus 8 completely customized strength training sessions doing the program we design based on that first session. And you’ll get to be a part of one of the most inviting, inclusive, and fun communities you’ll find anywhere. At the end of your trial, you get to decide if you liked it and if you want to continue with a regular 6-month membership. All the options and prices are on our Membership page.
You might also enjoy these posts . . .